What Is the Gut Microbiome?
by Dave Johnson · Published · Updated
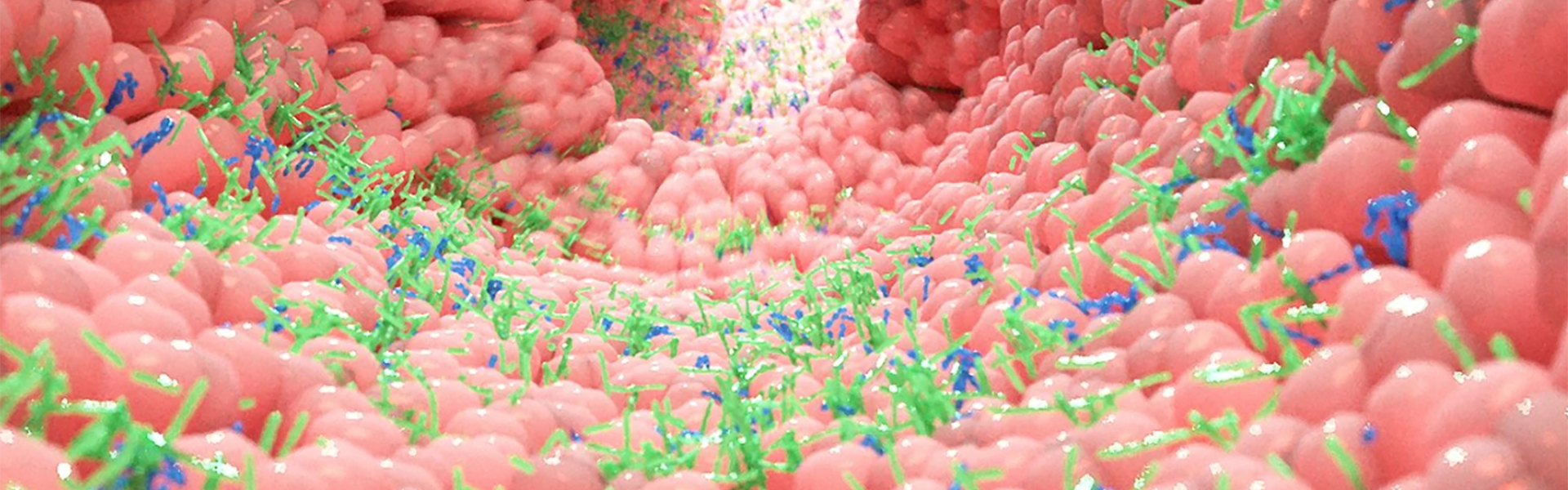
Bacteria, viruses, fungi and other microscopic living things are referred to as microorganisms, or microbes, for short.
Trillions of these microbes exist mainly inside your intestines and on your skin.
Most of the microbes in your intestines are found in a “pocket” of your large intestine called the cecum, and they are referred to as the gut microbiome.
Although many different types of microbes live inside you, bacteria are the most studied.
In fact, there are more bacterial cells in your body than human cells. There are roughly 40 trillion bacterial cells in your body and only 30 trillion human cells. That means you are more bacteria than human (1Trusted Source, 2Trusted Source).
What’s more, there are up to 1,000 species of bacteria in the human gut microbiome, and each of them plays a different role in your body. Most of them are extremely important for your health, while others may cause disease (3Trusted Source).
Altogether, these microbes may weigh as much as 2–5 pounds (1–2 kg), which is roughly the weight of your brain. Together, they function as an extra organ in your body and play a huge role in your health. Healthline
An excellent article:
The Ultimate Guide to Gut Health – by Vanessa Milne
Avini + Fiber the ultimate fiber supplement:
Greatest benefits if taken 15 minutes before meals.
Bulking fibers form gel matrix to give a “full’ feeling.
Delays gastric emptying, leading to better nutrient absorption.
Binds bile salts and acids to reduce LDL cholesterol production.
Delays absorption to lower postprandial hyperglycemia
Insoluble fiber improves digestive motility.
Inulin acts as a prebiotic – reducing bloating and gas.
Bicarbonate ‘fluffs’ up the gel matrix and provides more room for absorption.
Zeolite acts as a digestive detoxifying agent and improves nutrient uptake.